Case 05: RGB LED
Contents
7. Case 05: RGB LED#

7.1. Introduction#
The RGB LED is a type of LED light, It is capable of emitting light in three different colours - red, green and blue. We are going to program the RGB LED to change among red, green and blue gradually in this lesson.
7.2. Components List#
Hardware#
1 × Pico:ed
1 × USB Cable
1 × Breadboard Adapter
1 × 83×55mm Breadboard
1× RGB LED
3 × 100Ω Resistors
N* Dupont Cables
7.3. Main Components#
RGB LED#
As we all know, the three primary colours of light are red, green and blue, and by combining these three colours in different combinations, all the colours can be synthesised. Similarly, RGB LEDs can be used in different combinations of brightness to create a myriad of colours.

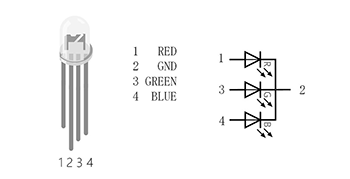
There are two types of tri-colour LEDs, common cathode and common anode: common cathode RGB LEDs are connected to GND; common anode RGB LEDs are connected to VCC; In this lesson, we use common cathode tri-colour LEDs.
7.4. Steps#
Hardware Connection#
Connect the RGB signal pins of the leds to the P0, P1 and P2 ports of the breakout board correspondingly, and connect a 100Ω resistor.
Connect GND to the breakout board GND through the breadboard.
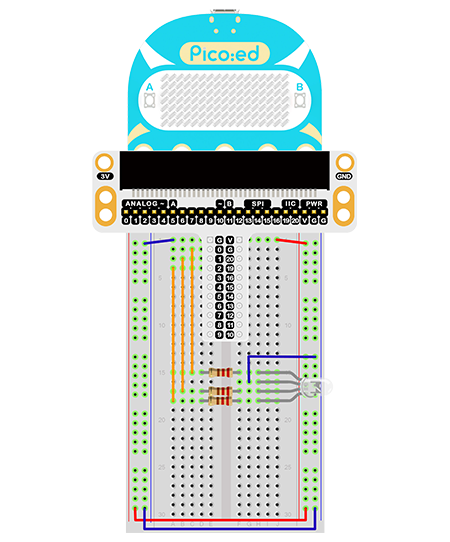
This is the picture after finishing the connections:
7.5. Programming#
Program Preparation: Prpgramming environment
Sample Code:#
# Import the modules that we need:
import board
import digitalio
import time
from picoed import button_a, button_b
# Set the connected pins and directions of the LEDs.
led_0 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P0)
led_1 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P1)
led_2 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P2)
led_0.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
led_1.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
led_2.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
# Judge if the button A/B is pressed with the equivalent operations.
while True:
if button_a.is_pressed() and button_b.is_pressed():
led_0.value = False
led_1.value = False
led_2.value = True
elif button_a.is_pressed():
led_0.value = True
led_1.value = False
led_2.value = False
elif button_b.is_pressed():
led_0.value = False
led_1.value = True
led_2.value = False
else:
led_0.value = True
led_1.value = True
led_2.value = True
time.sleep(0.1)
Details of the Code:#
Import the modules that we need.
boardis the common container, and you can connect the pins you’d like to use through it. Thedigitaliomodule contains classes to provide access to basic digital IO.timeis the module contains the fuction of time setting.
import board
import digitalio
import time
from picoed import button_a, button_b
Set the pins and directions of the breadboard adapter connecting to the LEDs
led_0 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P0)
led_1 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P1)
led_2 = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.P2)
led_0.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
led_1.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
led_2.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
If the pins you are using are not P0_A0 and P1_A1, the other pin numbers can be viewed by entering the following code in the shell window below the Thonny editor.
>>> import board
>>> help(board)
object <module 'board'> is of type module
__name__ -- board
board_id -- elecfreaks_picoed
BUZZER_GP0 -- board.BUZZER_GP0
I2C0_SDA -- board.BUZZER_GP0
I2C0_SCL -- board.I2C0_SCL
BUZZER -- board.BUZZER
BUZZER_GP3 -- board.BUZZER
P4 -- board.P4
P5 -- board.P5
P6 -- board.P6
P7 -- board.P7
P8 -- board.P8
P9 -- board.P9
P10 -- board.P10
P11 -- board.P11
P12 -- board.P12
P13 -- board.P13
P14 -- board.P14
P15 -- board.P15
P16 -- board.P16
SDA -- board.SDA
P20 -- board.SDA
SCL -- board.SCL
P19 -- board.SCL
BUTTON_A -- board.BUTTON_A
BUTTON_B -- board.BUTTON_B
SMPS_MODE -- board.SMPS_MODE
VBUS_SENSE -- board.VBUS_SENSE
LED -- board.LED
P0_A0 -- board.P0_A0
P0 -- board.P0_A0
A0 -- board.P0_A0
P1_A1 -- board.P1_A1
P1 -- board.P1_A1
A1 -- board.P1_A1
P2_A2 -- board.P2_A2
P2 -- board.P2_A2
A2 -- board.P2_A2
P3_A3 -- board.P3_A3
P3 -- board.P3_A3
A3 -- board.P3_A3
Judge if the button A/B is pressed with the equivalent operations. While button A being pressed, set the value of led_0 as true, the led_1 and led_2 as false. In the same way, program when button B being pressed and when button A+B being pressed
while True:
if button_a.is_pressed() and button_b.is_pressed():
led_0.value = False
led_1.value = False
led_2.value = True
elif button_a.is_pressed():
led_0.value = True
led_1.value = False
led_2.value = False
elif button_b.is_pressed():
led_0.value = False
led_1.value = True
led_2.value = False
else:
led_0.value = True
led_1.value = True
led_2.value = True
time.sleep(0.1)
7.6. Result#
Press button A, the LED turns red; B for green; A+B for blue.
7.7. Exploration#
If we want it to light in cyan, magenta, and yellow, how to design and program?
